
Greetings all anatomy students. There has been a dry spell of lessons this summer while I attended to blueberry crops and fruit trees! Berries are now done for the year and time to return to Outlander. Yay!
So, let’s get right to it.
During Episode 606, The World Turned Upside Down, Claire becomes deathly ill, not from what ails the MacNiel family, but from Malva Christie poisoning! 😈 😳
During an intense fever dream, Claire has a vision of roiling clouds and an amoeba. But then, her hands cradle something red and pulsing – her beating heart in this startling and somewhat gruesome image:
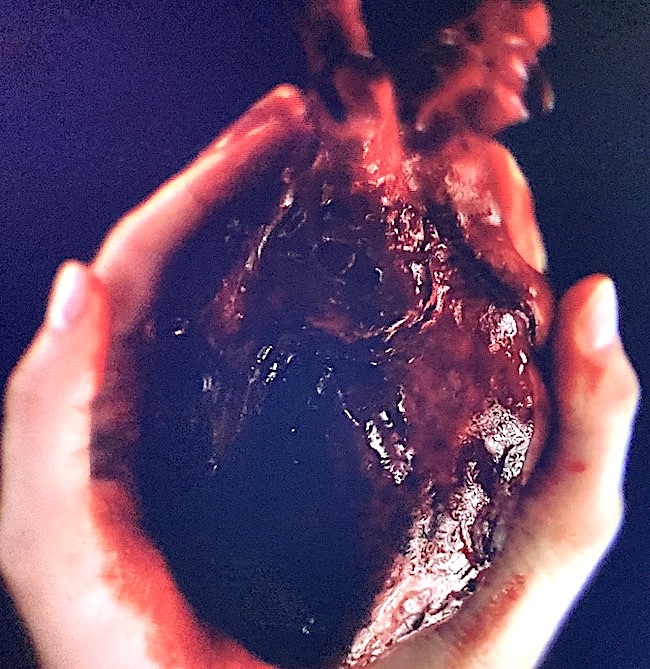
Fortunately, the show’s FX provides me with a splendid opportunity to teach students about the heart, a complex and essential organ. Oh, goodie! 😜
Learn: So, let’s study the heart!
This Mini Lesson will cover heart size, shape, position, apex, base, chambers, valves, cardiac muscle, and blood flow. Because the heart is fairly complex, I will try to keep the explanations as compact and useful as possible. 🤓
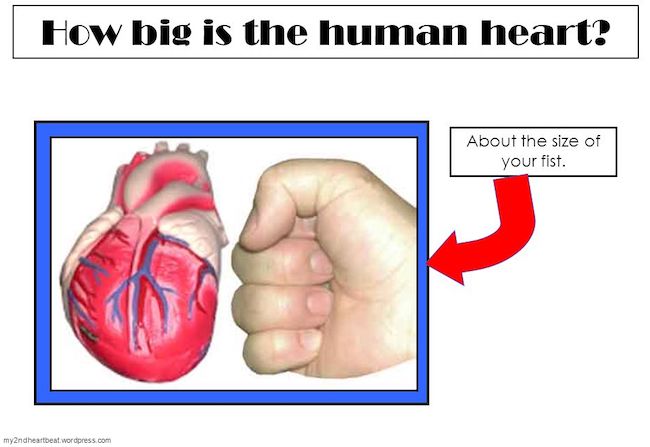
Size: First, how big is the human heart? The human heart is roughly the size of the person’s closed fist. ✊🏻 Thus, a man’s heart is usually slightly larger than a woman’s and both are larger than a child’s.
Try This: Make a fist and take a keek at it. It is likely close to the size of your own heart. If you are female, ask a male family member or friend to make a fist and explain what it means. Ditto for a child in your life.
Fun Fact #1: We sometimes compliment a generous person saying they having a “big heart.” But this is just a figure of speech. One doesn’t really want a big heart because a smaller heart is usually a healthier heart. Interestingly, people who exercise regularly tend to have smaller hearts that beat more efficiently. However, recent studies show some premier athletes who vigorously engage in prolonged exercise may have a slight enlargement of the heart muscle, but this is a somewhat unique situation.
Shape: What shape is the heart? I think it is worth while to point out that the heart is not shaped like a Valentine! 😉 Overall, its shape is so complex it is a bit challenging to explain. But, let me give it a try.

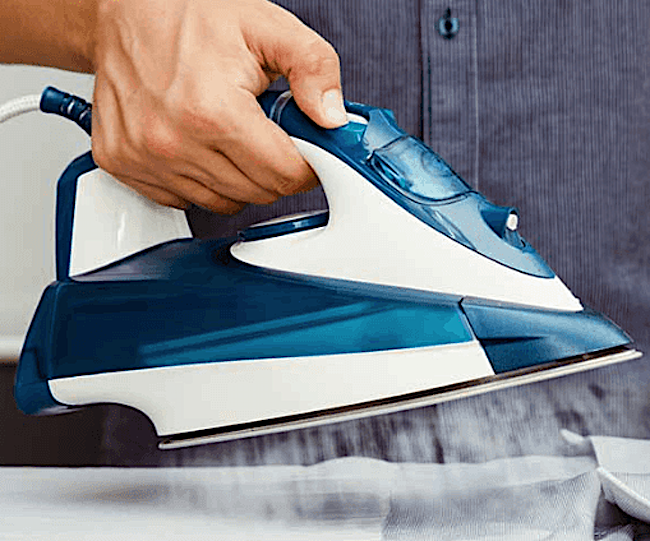
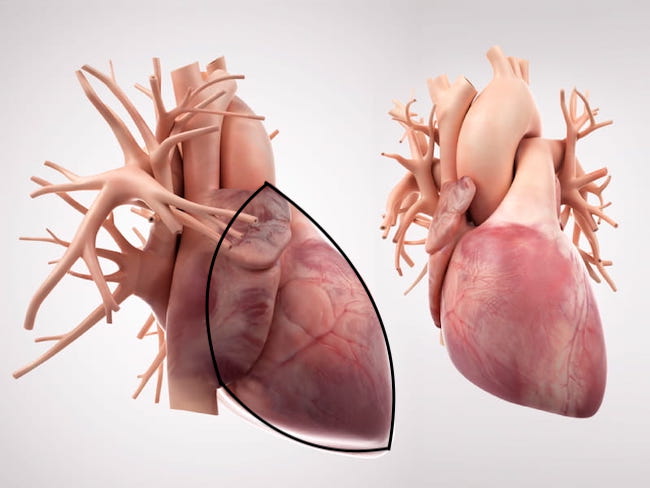
Alrighty then. If the heart is NOT shaped like a Valentine, what is its shape? Turns out, the heart is shaped something like a squat, plump hand iron without a handle! Yep. 👍🏻

Here it is from a frontal view. The heart is outlined in black. It is a bit difficult to visualize because the heart is somewhat obscured by the many vessels leading to and from it. (The right view shows the heart from behind)
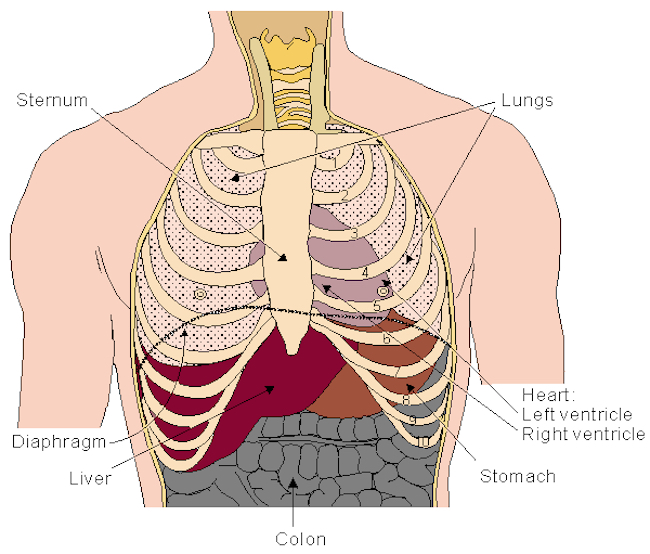
Position: Now, exactly where does the heart reside in the body? It sits in the chest nestled between right and left lungs and just above the respiratory diaphragm (black line in next figure).
About 2/3 the heart lies behind the sternum (breast bone) and about 1/3 projects to the left of the sternum with a wee bit to the right.
The heart does have a point but it is not directed downward as seen in Episode 606 (and many other films), but toward a person’s left side – bear in mind the hand iron image!
Apex: The point of the heart is its apex. The apex lies at the 5th intercostal space (between the 5th and 6th ribs), a little below the nipple (but, only if the breast is high). It is nearer the rib cage than the rest of the heart making the 5th intercostal space an important landmark for hearing the heart beat.
Base: The heart has a base but it is not the surface nearest the diaphragm, as one might expect. Rather, the base is opposite the apex and lies nearer the right lung.
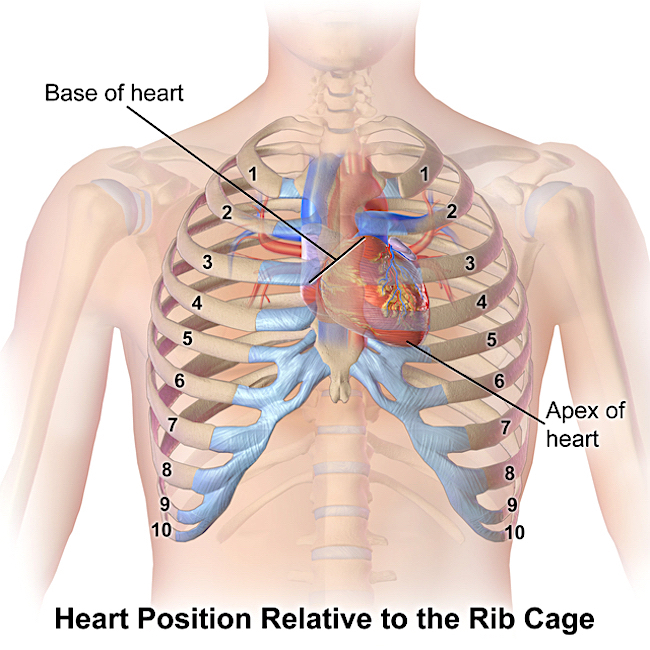
Next is a closer view of the heart nestled between left and right lungs (shown in pale pink). The black arrow marks the apex of the heart and the red arrow marks its base. Notice there is a distinct notch in the left lung to accommodate the apex; this is the cardiac notch. Again, the respiratory diaphragm is not shown in the image, but it lies directly under the heart.
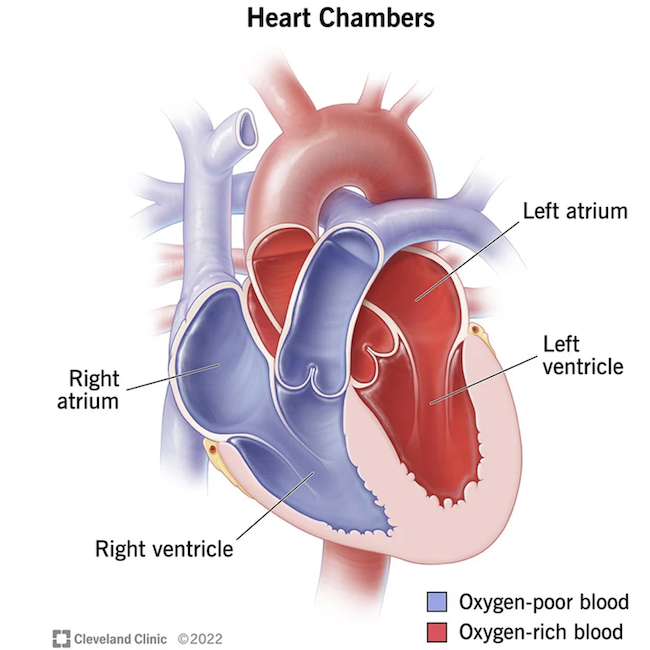
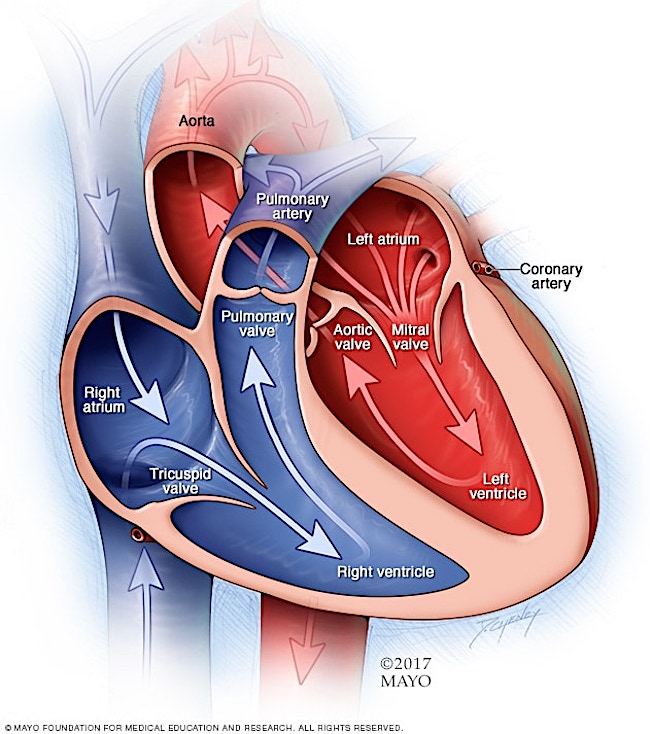
Chambers: The human heart is divided into four chambers, each designed to receive blood. Two smaller chambers that form the base are the atria (pleural of atrium). The ventricles are two larger chambers that form the apex and sides of the heart. These chambers are named: right (R) and left (L) atria and R and L ventricles; each plays a unique role.
In the cut-away view below, we see all four chambers. Notice these are on opposite sides than the viewer’s heart because the image is designed for a health care practitioner viewing the heart of a patient. 🤒
In digital images, the chambers are usually color-coded. R atrium and R ventricle are blue whereas L atrium and L ventricle are red. This color designation indicates oxygen levels of the blood in each chamber.
Bottom Line: The R two chambers are blue meaning they contain oxygen-poor blood that has just returned from the body (head, limbs, trunk). The L two chambers are red indicating they contain oxygen-rich blood that has just returned from right and left lungs.
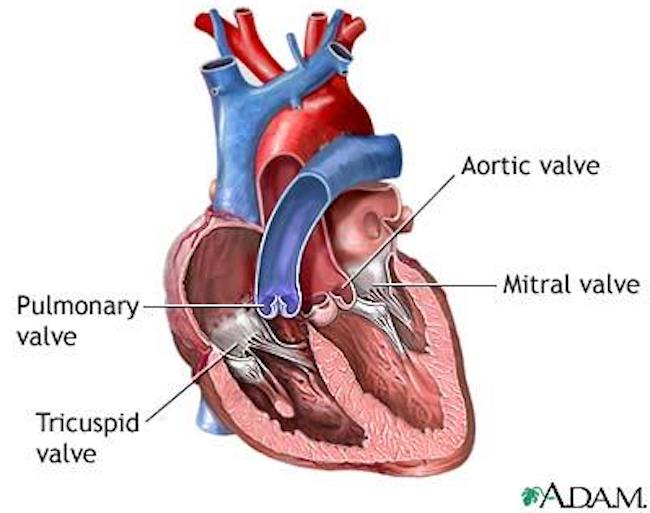
Valves: The heart is also equipped with four valves which control the flow of blood passing through the chambers. If a valve is open, the blood flows through it. If a valve is closed, then blood cannot back flow. 🚫
The four valves are (next image):
-
- Tricuspid Valve: This valve has three flaps and lies between R atrium and R ventricle.
- Mitral (Bicuspid) Valve: This valve has two flaps and lies between L atrium and L ventricle.
- Pulmonary Valve: This valve has three pockets and lies between R ventricle and pulmonary artery (leading to the lungs).
- Aortic Valve: This valve has three pockets and lies between left ventricle and aorta (carries blood to the head, limbs and trunk).
Cardiac Muscle: Just a note about heart (cardiac) muscle. Cardiac muscle is a special tissue only found in the heart. It has the ability to contract. It is thicker in the ventricles and thinner in the atria because the ventricles work harder to pump blood through the lungs and the body. The atria have thinner walls because their lighter workload consists of moving blood into their respective ventricles. Impulses from specialized cells stimulate cardiac muscle to rhythmically contract. We call this cycle of contraction and relaxation, the heart beat or cardic cycle.
OK, this ends the basic anatomy (although, there is much more). So let’s look as how the heart works.
Blood Flow: The heart is a pump. Similar to a pump that pushes water through a hose, the heart contracts rhythmically to pump blood through our vessels. As long as the heart continues to pump, blood continues to flow, delivering life-giving oxygen and nutrients to tissues and cells and removing carbon dioxide and waste products.
Our hearts only work if our vessels form a continuous loop. If a vessel is cut or disrupted, then blood seeps through the opening; if blood loss is significant, then pressure falls and the heart can no longer pump normally. This explains why injury of a major vessel must be cared for ASAP.
FUN FACT #2: The human body contains some 60,000 miles of blood vessels – enough to encircle the earth 2.5 times! The heart works hard to pump blood through this vast network.
FUN FACT #3: Each day the average heart beats 100,000+ times and pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood. In a 70-year lifetime, an average human heart beats more than 2.5 billion times! Super star! 🤩
How it Works: The heart is designed to receive blood via its atria and deliver blood via its ventricles (see image below). There really isn’t a simple way to describe this complex process but let’s give it a go! 👍🏻
-
- R Atrium: Oxygen-poor blood from the body is delivered to the R atrium via two large vessels (superior and inferior vena cavae). The R atrium contracts, the tricuspid valve opens, and blood pours from R atrium into R ventricle.
- R Ventricle: The R ventricle contracts, the tricuspid valve closes, and blood exits through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery whose branches deliver blood to R and L lungs (where it rids itself of carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen).
- L Atrium: Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs is delivered to the left atrium by pulmonary veins. The L atrium contracts, the mitral valve opens, and blood pours from L atrium into L ventricle.
- L Ventricle: The L ventricle contracts, the mitral valve closes, and blood exits through the aortic valve into the aorta whose branches deliver oxygen-rich blood to the body.
Cardiac Cycle: Now that you know what each side of the heart does, let’s see how the sides work together. Keeping in mind what each chamber does, understand that both atria contract simultaneously followed by both ventricles. The span of one heart beat to the next is the cardiac cycle.
Lub-Dub: The heart beat is described in anatomy and medicine as a lub-dub sound. Lub-dub sounds are close together followed by a brief pause. These sounds are caused by blood striking closed valve flaps.
-
- Lub sound is caused by blood striking tricuspid and mitral valves as they close, simultaneously.
- Dub sound is created by blood striking pulmonary and aortic valves as they close, simultaneously.
This video offers a good representation of the cardiac cycle. Watch for the contraction of atria and ventricles and then the pause. Also, watch valve flaps open and close as the heart chambers contract. In this animated film, only the cardiac vessels, which bring blood to and remove blood from the heart, are color-coded blue and red.
Try This: If you have a stethoscope, place it under the left fifth rib, in line with the nipple and listen for the lub-dub sounds. If you don’t have this tool, ask a partner or your child to lay down and place your ear in the same spot and try to hear the sounds of the valves closing. This is a totally awesome experience, especially if you know what it means!
This animated video helps us to further understand the cardiac cycle – you know the trope, “a picture is worth a thousand words.”
Fun Fact #4: I suspect you all know that heart disease is the leading cause of death in men AND women, worldwide. But, recently it has been found that some Old Order Amish people have a rare genetic mutation which reduces the risk of heart disease by 35%! The gene has been duplicated in mice. Efforts are now underway to produce a drug that may reduce heart disease in the same way as the gene mutation. Let’s hope it works! 🤞🏻
I hope now you have a better understanding of and appreciation for your own heart. We sort of take it for granted that hearts will always be there working for us. But, the heart is susceptible to disease and is not an easy organ to understand. Its embryology is even more complex which accounts for the frequency of cardiac birth defects. You did well, though. Keep up the good work!
Whew! 😅
Read about Claire’s beating heart in Diana’s sixth big book, “A Breath of Snow and Ashes.” This passage vividly describes her wild fever dreams as her body battles the infection planted by Malva. In Claire’s dream, her heart is the main character!
I seldom knew whether my eyes were open or closed, nor whether I woke or slept. I saw nothing but a roiling gray, turbulent and shot with red. The redness pulsed in veins and patches, shrouded in the cloud. I seized upon one crimson vein and followed its path, clinging to the track of its sullen glow amid the buffeting of thunder. The thunder grew louder as I penetrated deeper and deeper into the murk that boiled around me, becoming hideously regular, like the beating of a kettledrum, so that my ears rang with it, and I felt myself a hollow skin, tight-stretched, vibrating with each crash of sound.
The source of it was now before me, throbbing so loudly that I felt I must shout, only to hear some other sound—but though I felt my lips draw back and my throat swell with effort, I heard nothing but the pounding. In desperation, I thrust my hands—if they were my hands—through the misty gray and seized some warm, moist object, very slippery, that throbbed, convulsing in my hands.
I looked down and knew it all at once to be my own heart.
I dropped it in horror, and it crawled away in a trail of reddish slime, shuddering with effort, the valves all opening and closing like the mouths of suffocating fish, each popping open with a hollow click, closing again with a small, meaty thud. 🤯
See Claire’s beating heart in Outlander Episode 606, “The World Turned Upside Down.”
Let’s all hope our hearts continue to serve us as long as possible. From my heart to yours! ♥️

The deeply grateful,
Outlander Anatomist
Follow me on:
-
- Twitter: @OutLandAnatomy
- Facebook: OutlandishAnatomyLessons
- Instagram: @outlanderanatomy
- Tumblr: @outlanderanatomy
- Youtube: Outlander Anatomy
Photo and Video Credits: Starz, Sony, Outlander Anatomy, www.arcreativemedia.com, www.bemfi.fi, www.commons.wikimedia.org, www.covenanthealth.com, www.en.wikipedia.org, garmentsteamerguide.com, www.heart.org, www.heartsearch.org.uk, www.Luxsontube.com, www.medlineplus.gov, www.slideplayer.com

Loved this! I’m a retired emergency medicine doc so I’ve thought a lot about hearts and cardiac disease and had multiple opportunities to run cardiac arrests course of my professional life. Keep up the good work!
I spent a hour or so trying to explain this to my mother last year so she could understand her diastolic dysfunction and why she was having heart failure despite a normal systolic ejection fraction. She didn’t want to look at simple photos like this. Only wanted me to explain it (and fix it). Thankfully she liked her cardiologist (and so did I). Sadly she died at 92 in May from heart failure…
Hi Dr. Toni. Thank you for taking time to comment. I am glad you enjoyed the lesson. As an emergency room physician, I know you will have had lots of experience with cardiac disease. I try hard to make my lessons understandable to the general public although my teaching background was with medical students in the fields of gross anatomy, embryology and histology (I am now retired after almost 40 years of teaching and research). I wish my lesson had been available to your mother – the basics are necessary to understand a condition like diastolic dysfunction otherwise the person has no context to understand. I am so sorry to hear of her passing, but she did live for a very long time. I hope her life was a happy one. Take good care.