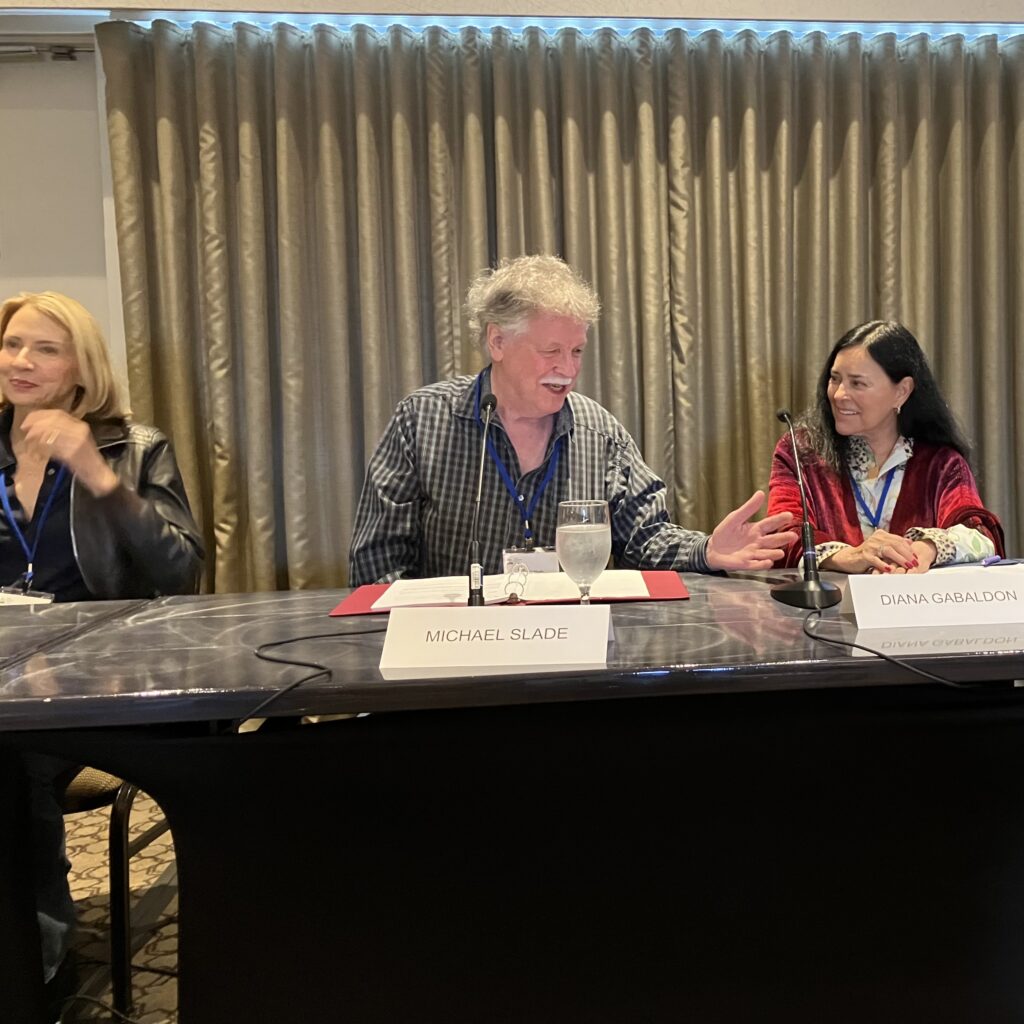
Good day, Diana fans!
On Sunday at Surrey International Writers’ Conference (SiWC) I was privileged to enjoy a long private lunch with Diana!
Details about our “date” are posted below but first a bit of history. The first time I lunched with Diana was 2015, almost 10 years ago!
We met in Beaverton, OR, after she spoke at a fund raiser. We have met for lunch or drinks many times since then.

The last time we lunched was at 2022 New York Comic Con. We began our outing by riding in a golf cart through the bowels of the Javits Center!
We enjoyed a delish lunch at Hudson Yards. Her nails this day were a beautiful dusty blue. BTW, these are her natural nails, not gels!
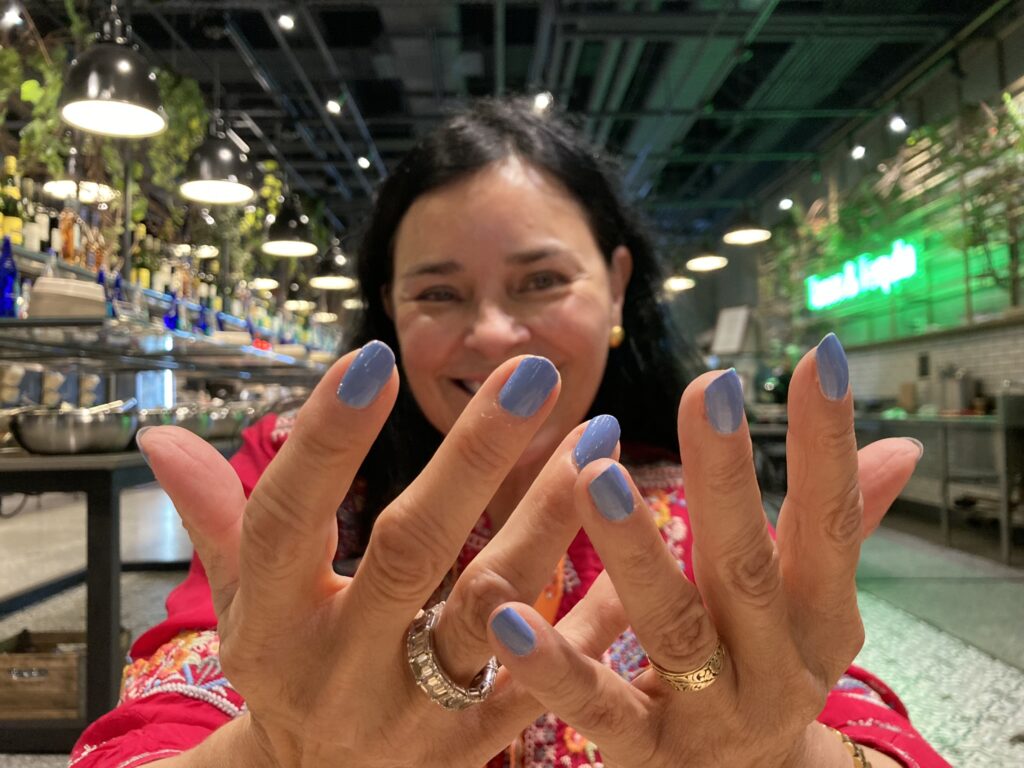
After lunch, we parted near The Vessel. It was a beautiful but windy day.
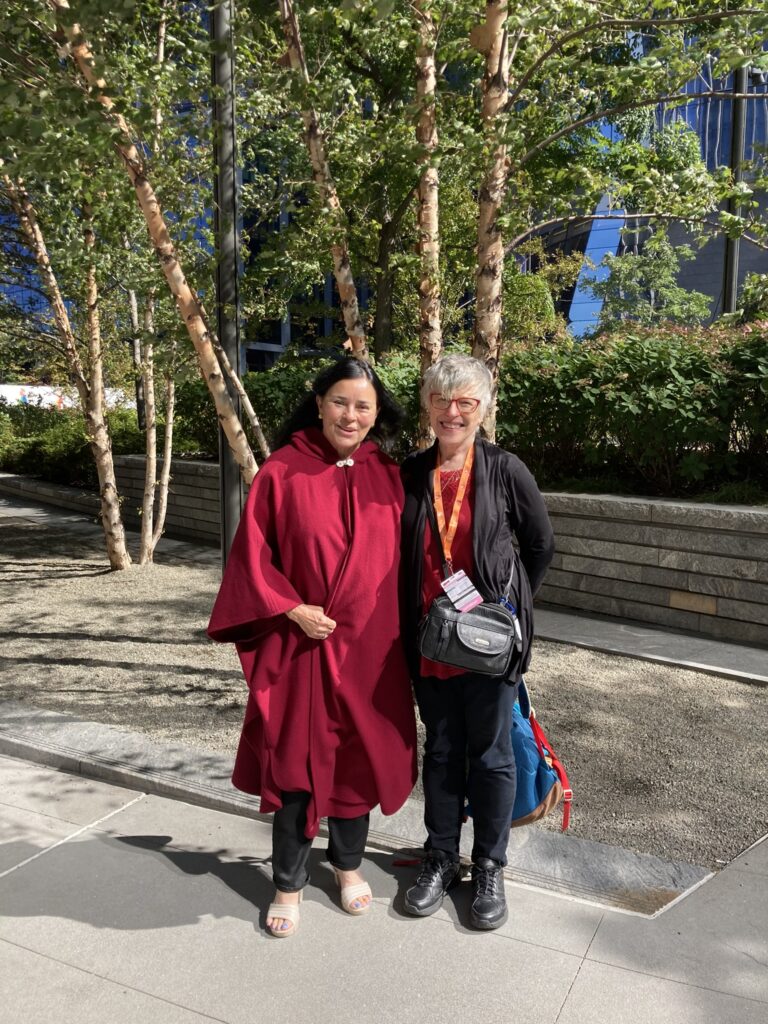

I had not seen Diana during 2023 because I spent that year rehabilitating a shattered ankle and didn’t go anywhere. 🥲
All of that changed at 2024 SiWC!
We had a wonderful two hour lunch on Sunday.
As we waited in line to be seated, author Michael Slade walked up and asked in a booming voice why women’s conversations were more interesting than men’s. I said I thought it is because women talk about everything while men have a fairly narrow range of acceptable topics. I was thinking sports, hunting, fishing, etc., for the guys. What do you think?
Diana and I ordered lunch. We were joined for a while by her youngest daughter, Jen. Hi Jen! 🤗
Jen lives in Scotland with her hubby and Diana’s two grandsons. She flew over just to attend SiWC. Sadly, she had to leave after a few minutes to catch her flight home. A delightful and very personable young woman. Mum was rightfully proud of her lovely daughter.
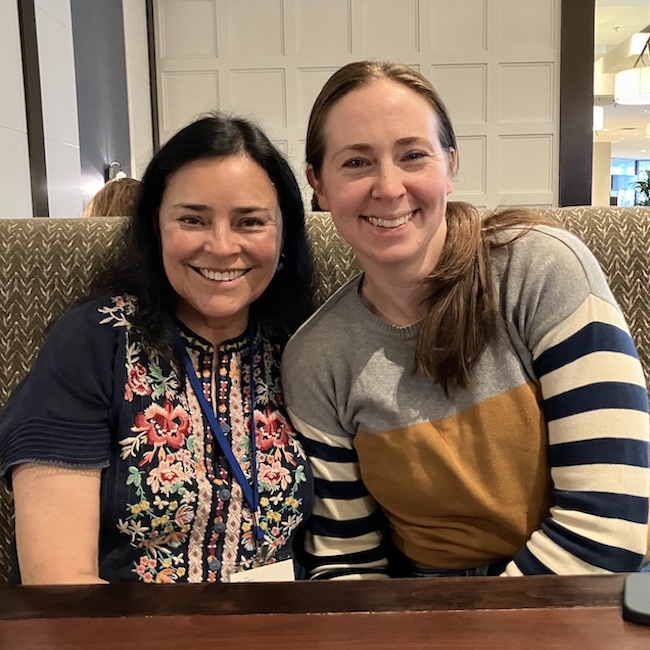

For the next 2 hours, we engaged in our usual discussion of far flung topics. Diana is very excited about Blood of My Blood (BOMB) and has written a couple of scripts for the show. She also gave the writers the ideas for it (of course)! 🤗
I asked her why it has taken 1.5 years between 7a and 7b. She answered that they were timing the releases of BOMB and 7b so there would not be issues with overlap.
We talked about our parents, our children and our lives growing up, our homes, property and pets. She shared photos of her darling grandsons (she is hoping for more).
She then commented on the beauty of the red and black bracelet I was wearing.
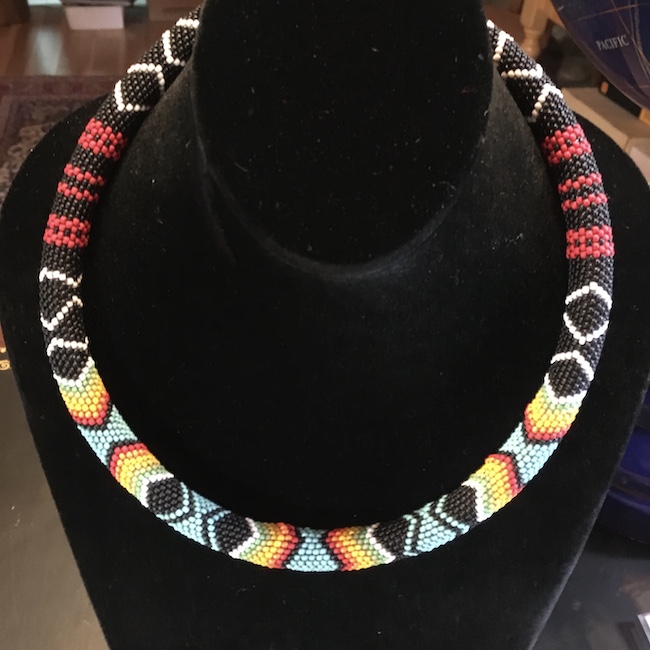
I make my own jewelry and she has received a number of pieces from me in the past, such as this one from 2019! 🎁
Sorry the photo is grainy. This is the piece on a form before I gifted it to her!

Back to my story. I removed the bracelet and said “Shall we try it on you?” I put it on her and asked if it was too big. She said it fit perfectly so I said “It is yours.” She was pleased! ☺️
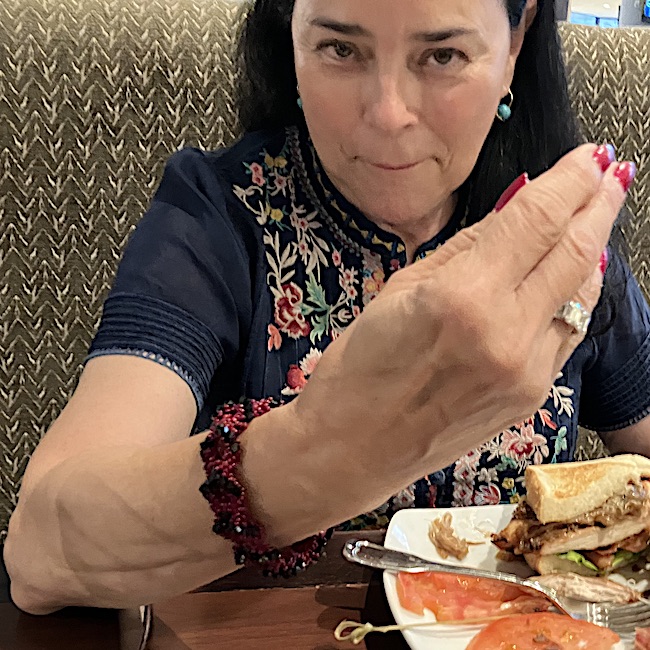
This felt uncanny because that very morning as I put the bracelet on, I thought, “I bet Diana is going to like this bracelet.” Then, I asked myself, “Do you want her to have it?” 🤔
Of course, the answer was “yes” as I can make myself another one. 😁
It made her happy! 🤗
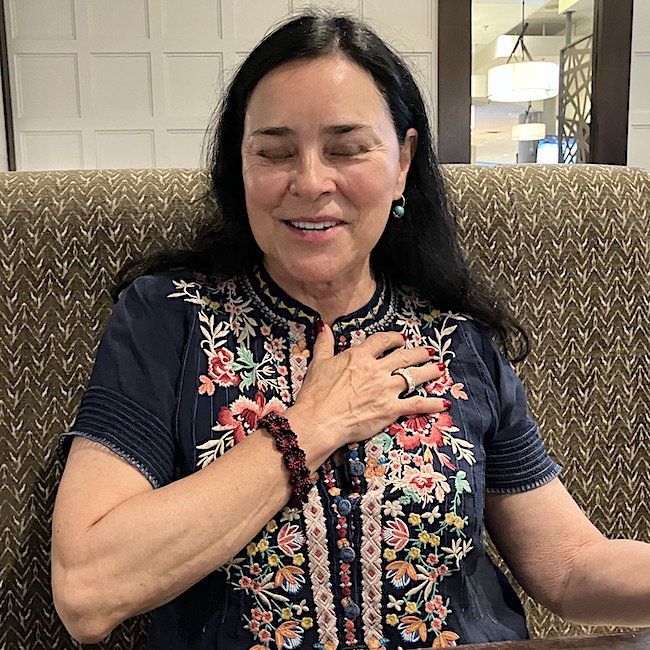
She let me photograph (a tradition of mine) her new nail color, a beautiful lush red. She usually wears lavender, blue or green. I think the color looks great on her. She wears jewel tones very well! 😍 Psst….Isn’t her top lovely?
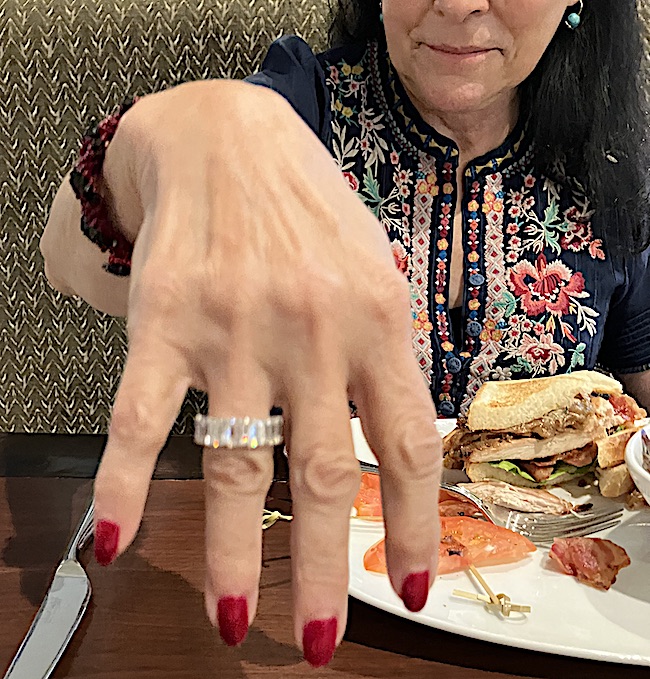
After two hours, she was tiring and I understood why. In just three days, she had done multiple events: Michael Slade’s Shock Theater, a library panel event, two solo workshops and an author’s panel. She also had done blue pencil events where she helps new authors with their work.
Her last 1.5 hour workshop occurred just before lunch and she had yet another event to attend that evening. The woman is a power house but she does need to rest sometimes! 😉
So we hugged and said farewell, until next time! 👋🏻
But wait! I have more. I will end my post with the next video.
Some of you are aware that during SiWC Diana does philanthropic work in the British Columbia prison system. She teaches a master class on writing to the inmates. This year she was unable to work with them because the contact she needs to help her access the system sadly passed away. So, in the future, she must find a new sponsor.
Although I made this video in 2018, it gives you an idea of the important work that Diana does for people whose lives are impacted by incarceration. She teaches her class and then listens to their questions and comments. Based on these, she buys and donates books to the prison library to help them with their goals.
Her works are a good lesson in kindness to all of us. 🥰
Isn’t she the best? 🤩
The deeply grateful,
Outlander Anatomist
Follow me on:
-
- Twitter: @OutLandAnatomy
- Facebook: OutlandishAnatomyLessons
- Instagram: @outlanderanatomy
- Tumblr: @outlanderanatomy
- Youtube: Outlander Anatomy
Video and Photo credits: Outlander Anatomy,


