Greetings anatomy students! Hanging is a ghastly topic, but it has a substantial presence in Outlander and is pertinent to anatomy. So, here we go!
The Oxford Dictionary defines hanging as “specifically to put to death by suspension by the neck.” But, in the past, hanging also meant death by crucifixion or impalement!
An interesting fact…. The appropriate terminology is the person was hanged, not the person was hung.
Outlander’s first traditional hanging appeared in episode 115, Wentworth Prison; crusty Taran MacQuarrie of the Watch and Jamie Fraser face their ends with stirring gallows’ humor: Jamie is afraid “My wife will never forgive me for getting myself foolishly hung!” Hanged, Jamie…. the word is hanged!
But, Taran aways knew he was fated to die at the end of a rope – his name is read next.
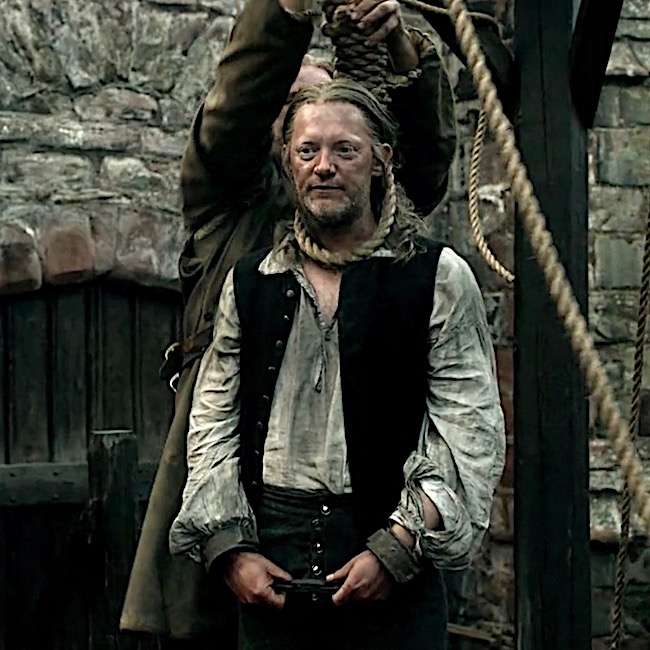

Jamie’s turn! Scribe, Liam McCallum, recorded Jamie as guilty of “a very extraordinary and abominable crime and most atrocious injury against us!” Snort!

Jamie struggles, but is subdued and resigns himself to this ignoble fate. Such an unworthy end for Laird Broch Tuarach!
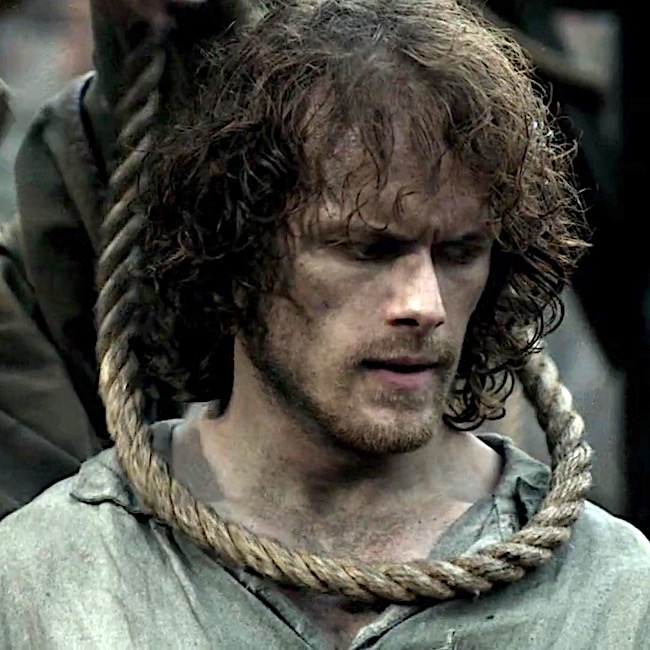

Then one of Lucifer’s avenging angels swoops in to spare Jamie for a different fate! But, this outcome awaits another lesson.

No further traditional hangings, until season four. Episode 401, America the Beautiful, starts off with a bang… Well, with a hangman’s noose, truth be told.
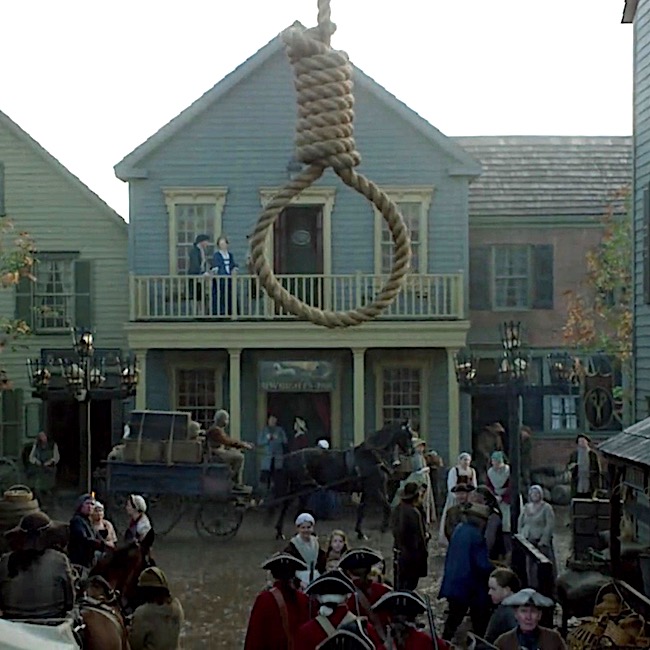

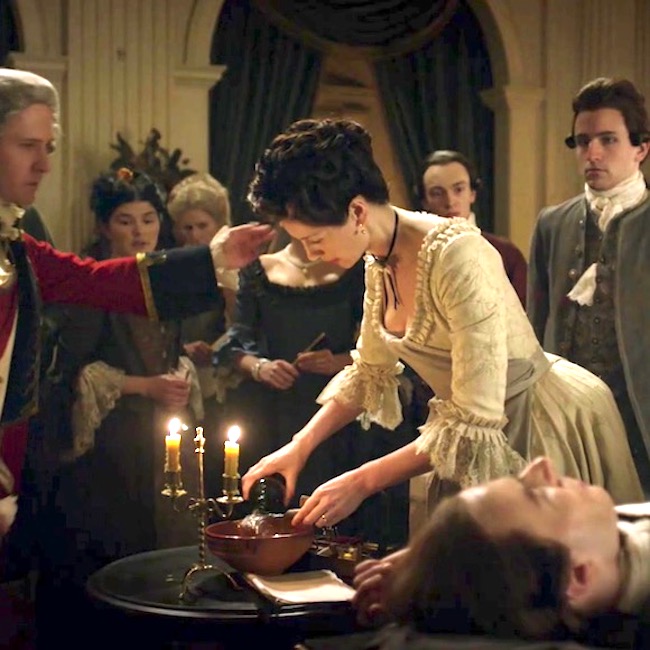
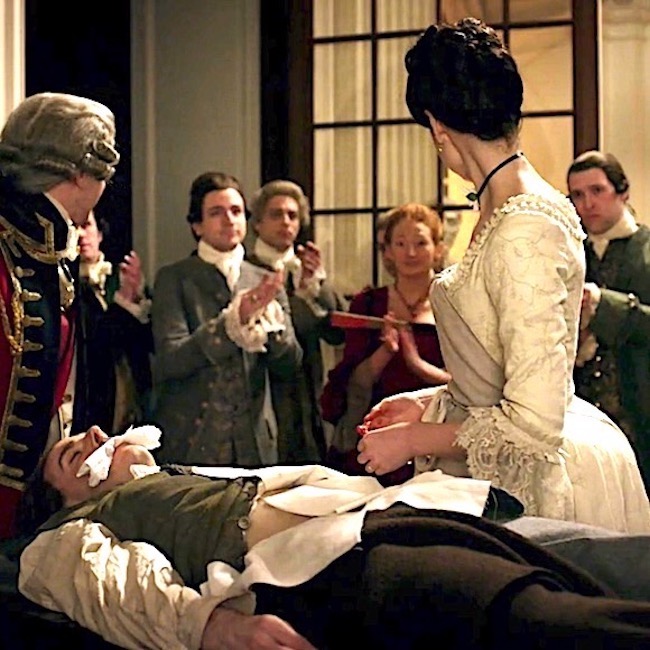
In a drunken state, Gavin Hayes lay with a marrit woman (psst…Jamie warned him!). When the outraged hubby came at him with a pitchfork, Gavin kicked him down the stairs and now, the hangman’s noose awaits. He should have listened to Mac Dubh! (In Drums of Autumn book, Gavin was guilty of stealing six pounds, ten shillings).
Hayes asks Jamie for two favors:
#1. Whisky!
Herself described in Drums of Autumn:
“It was what he asked of me,” he said. “And the best I could manage for him.”
“Brandy or whisky?” asked Fergus, evaluating Hayes’ appearance with a practiced eye.
“The man’s a Scot, wee Fergus.” Jamie’s voice was as calm as his face, but I heard the small note of strain in it. “Whisky’s what he wanted.”
“A wise choice. With luck, he won’t even notice when they hang him,” Fergus muttered
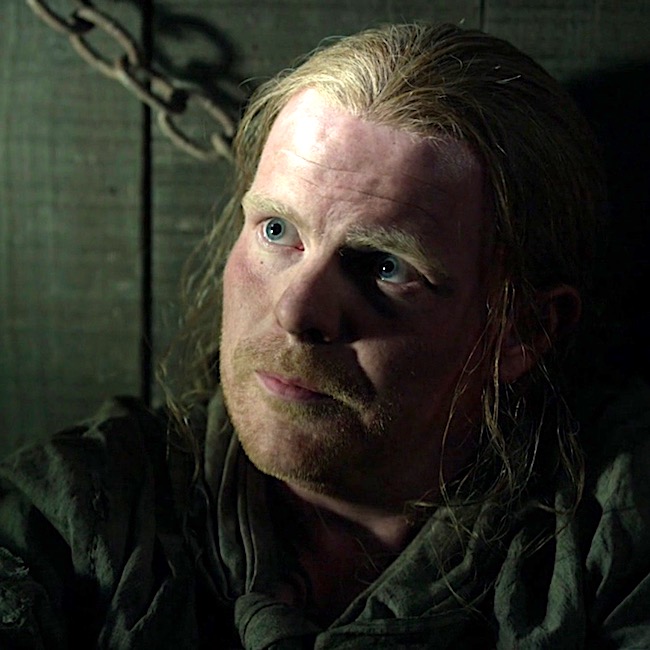

#2. May his last sight be the face of a friend.
Again, from Drums of Autumn:
If Hayes was still sober enough to see anything, the last thing he saw on earth would be the face of a friend.
He could see; Hayes glared to and fro as they lifted him into the cart, twisting his neck, desperately looking.
“Gabhainn! A charaid!” Jamie shouted suddenly. Hayes’ eyes found him at once, and he ceased struggling.
Jamie musters a wan smile for his auld friend and fellow Ardsmuir prisoner.
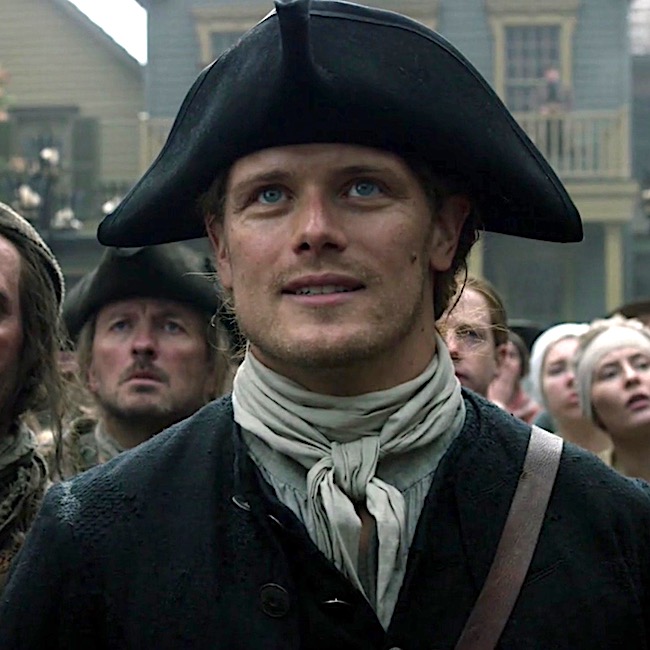

Drums of Autumn quote continues:
The captain of the guard stood poised, saber raised.
Suddenly, the condemned man drew himself up straight. Eyes on Jamie, he opened his mouth, as though to speak.
The saber flashed in the morning sun, and the drums stopped, with a final thunk! I looked at Jamie; he was white to the lips, eyes fixed wide. From the corner of my eye, I could see the twitching rope, and the faint, reflexive jerk of the dangling sack of clothes. A sharp stink of urine and feces struck…
The rope drops. Hayes death appears mercifully quick! Again from Drums of Autumn:
The hangman had known his business; there had been no undignified struggle, no staring eyes, no protruding tongue; Gavin’s small round head tilted sharply to the side, neck grotesquely stretched but cleanly broken.
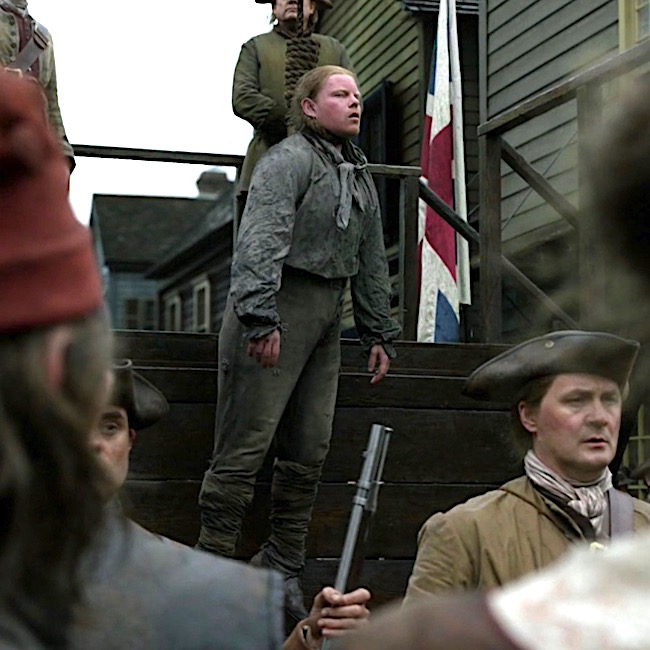

OK, but, what about non-traditional hangings? Any of these in Outlander. But, of course!
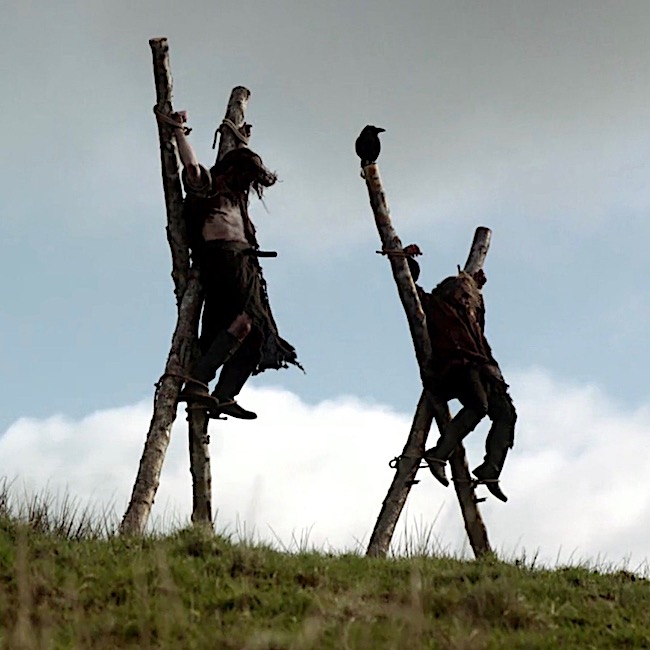
Two Jacobite traitors hang from crossed stakes courtesy of Red Coats in Outlander episode 105, Rent. Dougal and his party find the dead men with “T” for traitor carved into their flesh. Although we don’t know how they died one can reasonably consider this a variation of a crucifixion hanging.

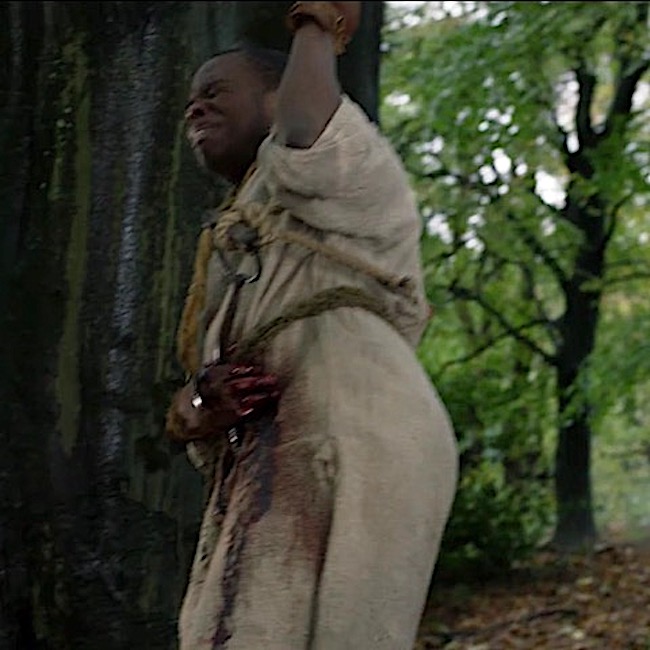
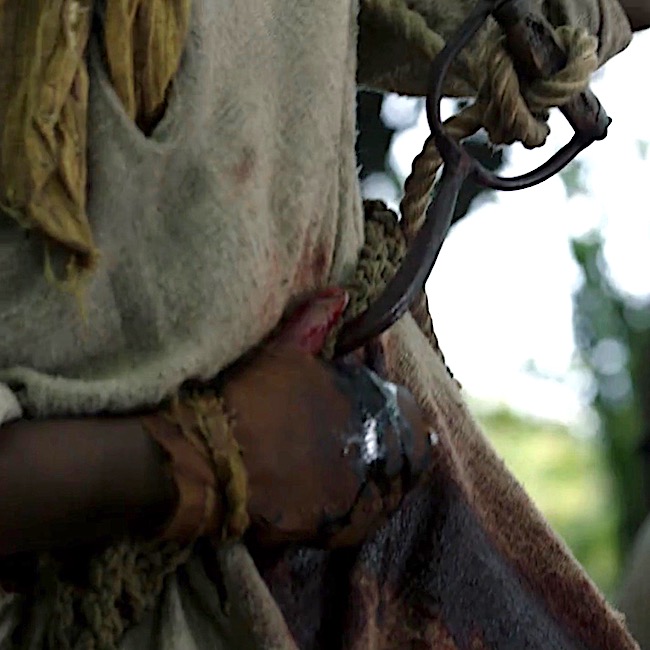
And, finally! In ep 402, Do No Harm, Jocasta’s slave, Rufus, dangles from a hook thrust under his ribs. This type of hanging is known as impalement.
From Drums of Autumn:
From everything I could sense and feel, I thought that the curve of the hook had gone upward through the liver. Likely the right kidney was damaged, and the jejunum or gallbladder might be nicked—but none of those would kill him immediately.

So, one may reasonably conclude that Outlander has dutifully presented both traditional and non-traditional hangings!
Now, on to anatomy! Waaay back, Anatomy Lesson #12, Claire’s Neck or The Ivory Tower, has a section on hanging but today we go deeper into the subject.
So, what does hanging have to do with human anatomy? Quite a lot actually, because hanging destroys normal anatomy. Let’s see how.
Understanding traumatic events from hanging requires a bit of neck anatomy. So….
Neck Anatomy: The neck is complex because it contains a mess of structures. These include:
-
- pharynx for food and air passage
- larynx for air passage and vocalization
- trachea for air passage
- esophagus for food passage
- common carotid arteries supply blood to head
- jugular veins drain blood from head
- cervical vertebrae for support
- hyoid bone for speech, swallowing, tongue movements
- cervical spinal nerves, for neck and upper limb innervation
- muscles for movement of head, neck, scapula and clavicle
Hangings typically traumatize one or more of these neck structures:
-
- cervical vertebrae
- hyoid bone
- carotid arteries
- jugular veins
- trachea and larynx
Cervical Vertebrae: The neck contains seven cervical vertebrae numbered from skull downward as C1-C7 (Image A). C1 is also known as the atlas; C2 is the axis.
Cervical vertebrae are smaller and more delicate than thoracic and lumbar vertebrae; this is especially true of C1 and C2. Collectively, all seven cervical vertebrae form the cervical skeleton and are bound together by strong ligaments.
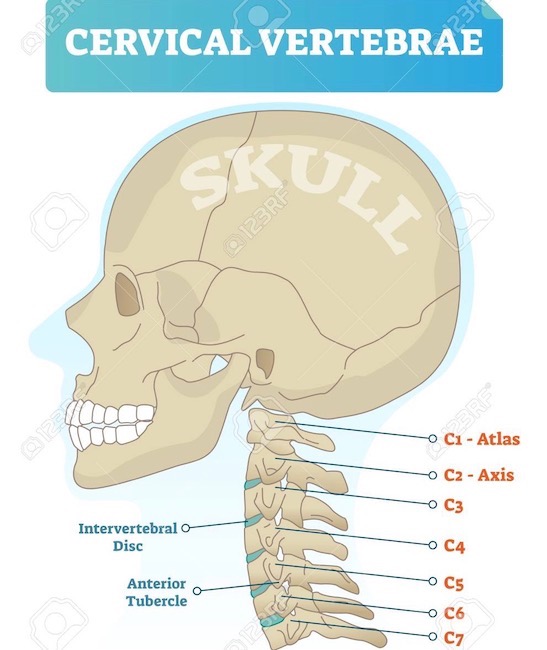
Image A
Hyoid Bone: The hyoid bone and cervical vertebrae are the only bones in the neck . The U-shaped hyoid (Image B, red) is unusual because it is the only bone of the body that does NOT articulate with other bones. Rather, it is suspended in the neck via muscles and ligaments connecting to neighboring bones and cartilages. More detail on hyoid and cervical vertebrae in Anatomy Lesson #12, Claire’s Neck – The Ivory tower.
Try This: You can palpate your own hyoid bone. Hold chin parallel to floor. Place thumb and forefinger of one hand on either side of your larynx (voice box). Move fingers upward until just under mandible. Squeeze gently, then swallow. You will feel a thin hard structure on each side, the R and L arms of the hyoid.
And, for book readers, Diana wrote about the hyoid bone in Written in My Own Heart’s Blood.
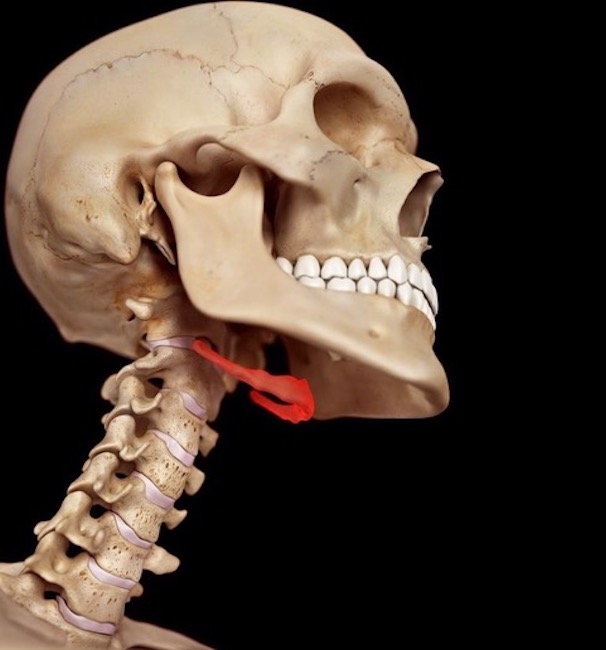
Image B
Common Carotid Arteries: The neck has a R and a L common carotid artery; each is a primary or secondary branch of the aorta arch (Image C). Common carotids straddle trachea and larynx (Image C -blue/green structures) before splitting into internal and external carotid arteries which supply blood to neck and head.
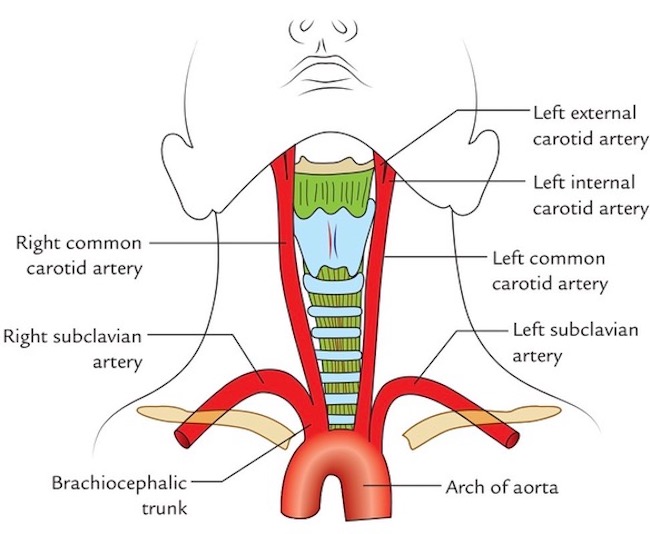
Image C
Jugular Veins: The neck has two jugular veins on each side; external and internal jugulars. These drain blood from head and neck structures toward the heart Image D).
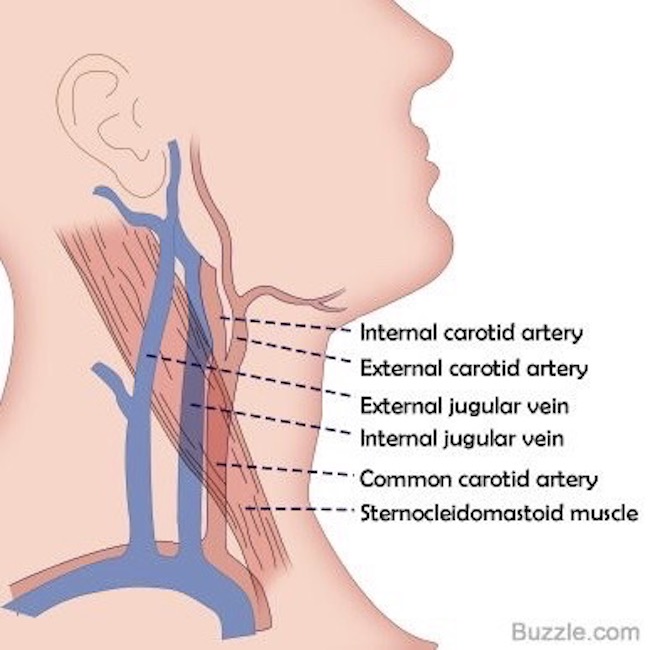
Image D
Trachea and Larynx: All of larynx plus upper trachea lie in the neck. Both are conduits for air to reach the lungs during inhalation and to leave the lungs during exhalation. In addition, the larynx produces vocalizations. Trachea and larynx provide the only normal route by which air can move to and from the lungs. Of course, a tracheotomy is an exception, but it is also not normal. (Psst…No S5 spoilers from book readers, please!)
Image E shows trachea and larynx. Tracheal wall is stiff due to cartilage plates. The complex larynx consists of nine cartilages of various shapes and sizes. Learn more about the larynx in Anatomy Lesson #42, “The Voice – No, not that One!”
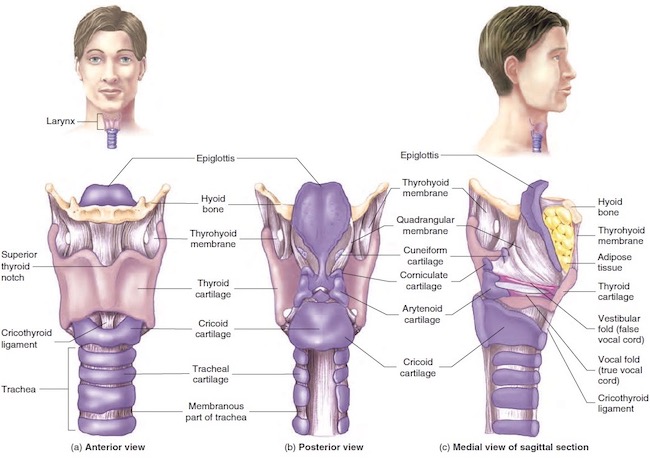
Image E
Now, for some info about hanging.
Hanging: One might think hanging is a rather simple act, but it is not. There are many types of hanging although death is typically from either strangulation or neck fracture. Here are three common types of hanging.
*Short Drop: A condemned person is placed on a stool, ladder, cart, horse, etc. with noose around the neck. The object is removed leaving the person dangling from the rope. Although the person is unconscious within 15 seconds, death usually takes 10-20 minutes as the noose tightens causing slow strangulation.
*Standard Drop: A condemned person drops 4-6 feet (1.2-1.8m). This is considered more “humane” than short drop because it typically fractures the neck which traumatizes spinal cord and causes immediate unconsciousness and rapid brain death.
*Long Drop: Drop varies. Height and weight of the condemned were used to calculate the drop needed to fracture the neck, preferably at C2, the axis. This is known as a hangman’s fracture.
Yes, I know! Horrifying to think about, but charts were developed to augment a swift death, the preferred outcome.
Submental Knot: Submental means “under the chin.” Careful placement of the eye or knot of the noose under the chin jerks the head backward, contributing to neck fracture. Side and back knots tend to strangle rather than fracture the neck.
For more information about the chin, read Anatomy Lesson #26, Jamie’s Chin – Manly Mentus.
Back to Outlander: So, with knowledge about vulnerable neck structures and types of hangings plus their effect on anatomy, let’s review Outlander hangings.
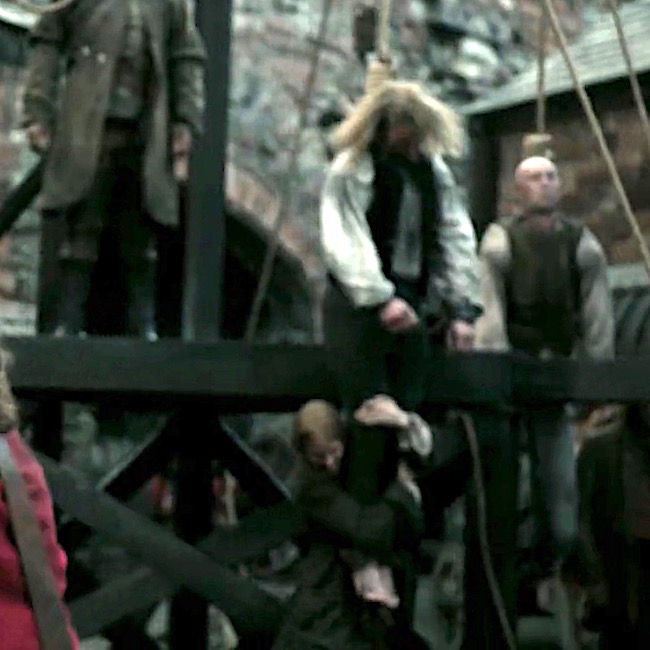
What about Taran from ep 115, Wentworth Prison? Taran was pushed off a not-very-tall scaffold – so in effect a short drop. Sadly, it didn’t break his neck and the Watchman kicked and struggled at the end of the noose! A member of the execution squad pulled down on his legs to break his neck, an act that was often required to end the misery. Of course, Jamie and other condemned prisoners witnessed this horror!

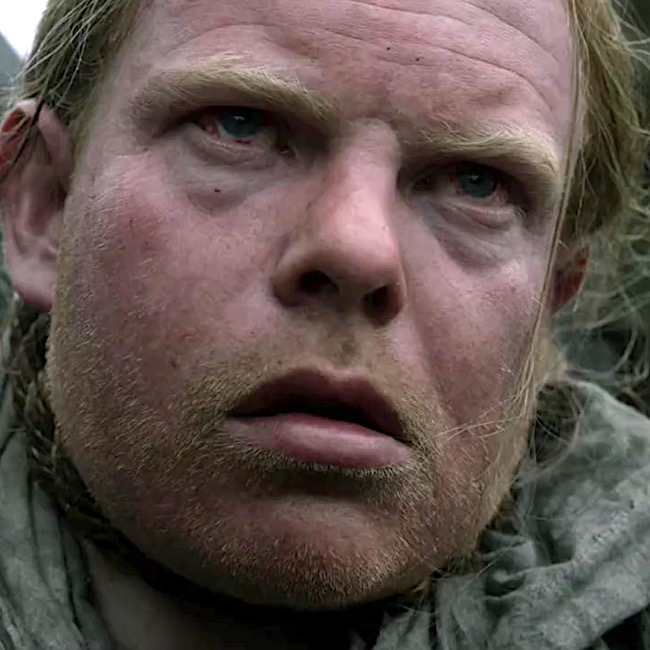
And, then there’s Hayes. Although his end was swift in Drums of Autumn book, not so in the episode. He did experience either a standard or long drop but afterward, his face is red and bloated and his eyes bloodshot. These findings are more consistent with strangulation than neck fracture, meaning his jugular veins were obstructed leading to death by brain edema and ischemia, wherein:
-
- Face becomes engorged with blood
- Facial skin turns red
- Facial skin exhibits tiny petechiae/petechia (small blood marks)
- Bleeding in conjunctiva overlying whites of eyeball (subconjunctival hemorrhage)
So the FX were very good but not well-matched for this type of hanging.
Just so we know, if the deeper lying common carotid arteries are occluded by strangulation, the face appears pale or white.
And, sphincters do relax spontaneously so urine and feces are evacuated. Thankfully, these weren’t part of the FX scheme! 😱

And poor Rufus! Impalement by hook is a very old punishment occurring in Babylonia! Later, it was used in 18th-century Ottoman-controlled Bosnia and by Dutch overlords in Suriname (South America) who impaled troublesome slaves under the ribs.
An 18th century observer recorded that an impaled person could hang as long as three days before expiring. The primary source of pain was extreme thirst. Thankfully, this type of hanging has been pretty much abandoned.

As for the hyoid bone…. It fractures in about a quarter of hangings but is not the cause of death. Forensic scientists look for a fractured hyoid in suspected homicides because about 50% of hyoids fracture with manual choking.
Fracturing the hyoid bone depends on applied force, age of victim, nature of instrument (ligature vs. hands) so even if the bone is not fractured, a murder is still possible (Image F – red arrow).
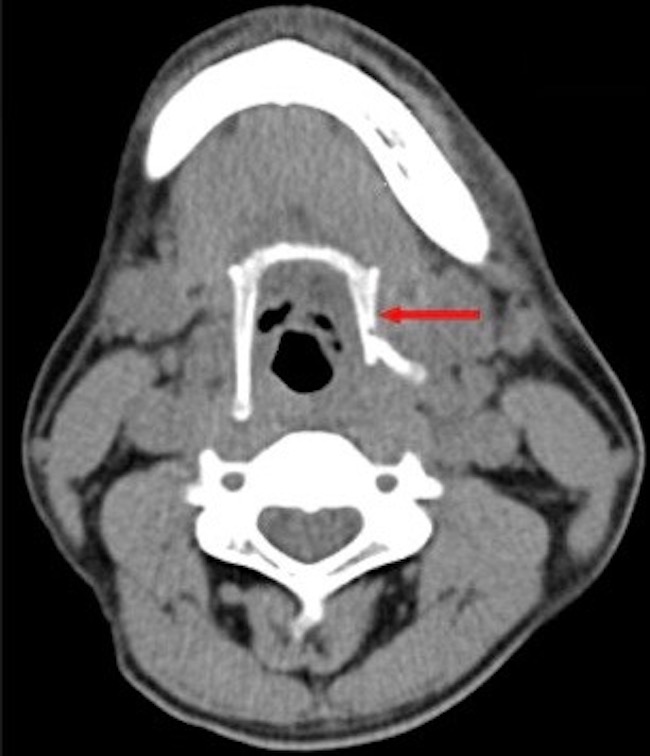
Image F
Today, we can be grateful that many countries have abandoned hanging as a means of punishment. An excellent film is available on this topic: Pierrepoint: The Last Hangman. Bonus! Tobias Menzies plays Lieutenant Llewelyn!
In Jamie’s time, hanging was an ignoble death. Why, we might ask? Here is one reasonable thought:
“The sword connoted an honourable way of dying, and an honourable return to the earth, but the rope left the body hanging between heaven and earth and was therefore an unseemly death.”
― Ron Brown, The Art of Suicide
Until next time….Hang in there!
The deeply grateful
Outlander Anatomist
Follow me on:
- Twitter @OutLandAnatomy
- Join my Facebook Group: OutlandishAnatomy
- Instagram: @outlanderanatomy
- Tumblr: @outlanderanatomy
- Youtube: Outlander Anatomy
Photo Credits:
- Starz
- www.123RF.com (Image A)
- www.verywellhealth.com (Image B)
- www.earthslab.com (Image C)
- www.socratic.org (Image D)
- www.brainkart.com (Image E)
- www.sciencedirect.com (Image F)