Anatomy Def: Pilus is the scientific term for a single hair; pili means multiple hairs
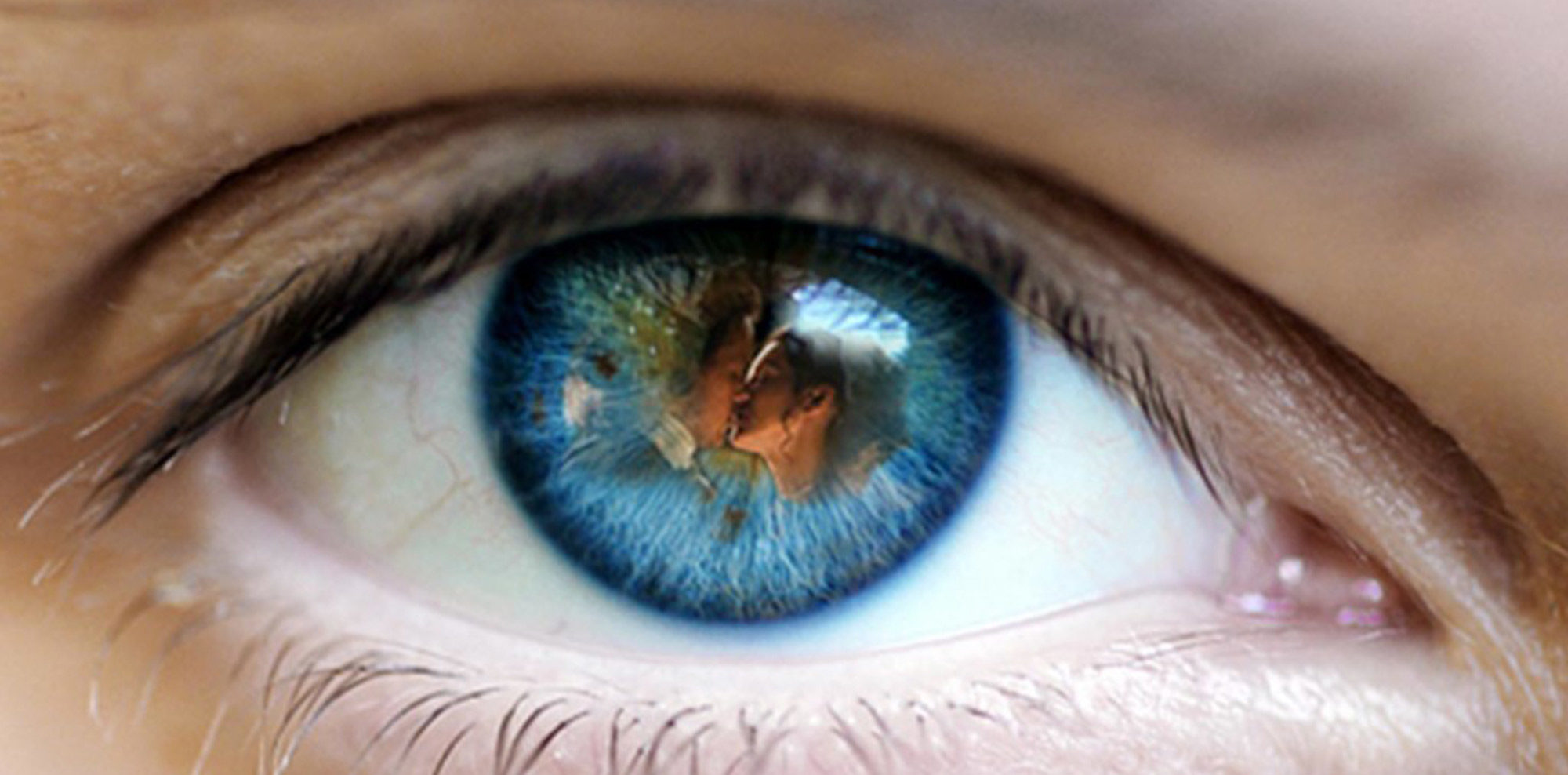
Outlander Def: Claire-hair forms a halo of curly pili! (psst… Jamie loves it!)
Learn about hair in great detail in Anatomy Lesson #6, “Claire’s Hair, Jamie’s Mane or Jesus H. Roosevelt Christ!”
Hey, anatomy students! How about a brief pilus quiz? No grading, I promise.
What type of pili inhabit your head? Turns out, there are different systems of classifications, but the following one is practical and easy.
Shape of your pili:
-
- Straight?
- Wavy?
- Curly?
- Coily?
- None? 😉
Type of pili strand:
-
- Fine?
- Medium?
- Coarse?
Amount of hair? (based on circumference of “full hair ponytail”). If you don’t have a ponytail, then guess.
-
- Thin (ponytail is 2” or less)
- Normal (ponytail is 2”-4”)
- Thick (polytail is > 4”)
How did you do? Wouldn’t you know it, all such characteristics have been described and worked out. 🤗 There are even subcategories of hair if you want to read more!
Pili are fascinating for many reason. First and foremost, pili are products of skin, our body’s largest organ! The skin of “average adults” weighs about eight pounds, with a surface area of 22 ft²! 😲 The larger one is, the more weight and more surface area is taken up by skin.
The skin is equipped with various appendages including pili, erector pili muscles , nails, and various glands.
Turns out, hair is far more complex than one might imagine. Read on for more fascinating deets!
Hair growth differs depending on body region (duh 😉):
-
- Glabrous: Regions sans hair – palms, soles, external genitalia, lips, back of ear, and scars.
- Terminal: Thick, coarse hair – beard, pubic area, eyelashes, brows, scalp.
- Vellus: Thin, fine, light-colored hair typical of childhood and adult women. In female adults found on eyelids, face, chest, etc. Vellus hair can convert to terminal hair under the influence of androgens.
Next, anatomy divides the pilus into two parts:
-
- Follicle: Part embedded in the dermis – the only living part of a hair.
- Shaft: Thin filamentous part that extends beyond skin surface – non-living part
Follicle: A follicle is the part of a pilus that lies below the skin surface. Pull out a strand of head hair, and observe a pale enlargement on the end that was embedded in skin – this is the bulb or root of the follicle. The shaft is produced by the root.
Follicles are lined with skin stem cells that can re-grow a hair after it is lost. It may also regrow skin after various wounds, such burns. Here, stem cells produce new skin cells that grow out of the follicle and spread across the damaged surface to help cover the injury. This is effective if the wound is relatively small; larger wounds may require skin grafts. Lastly, the new skin is a type of scar tissue which does not regrow appendages.
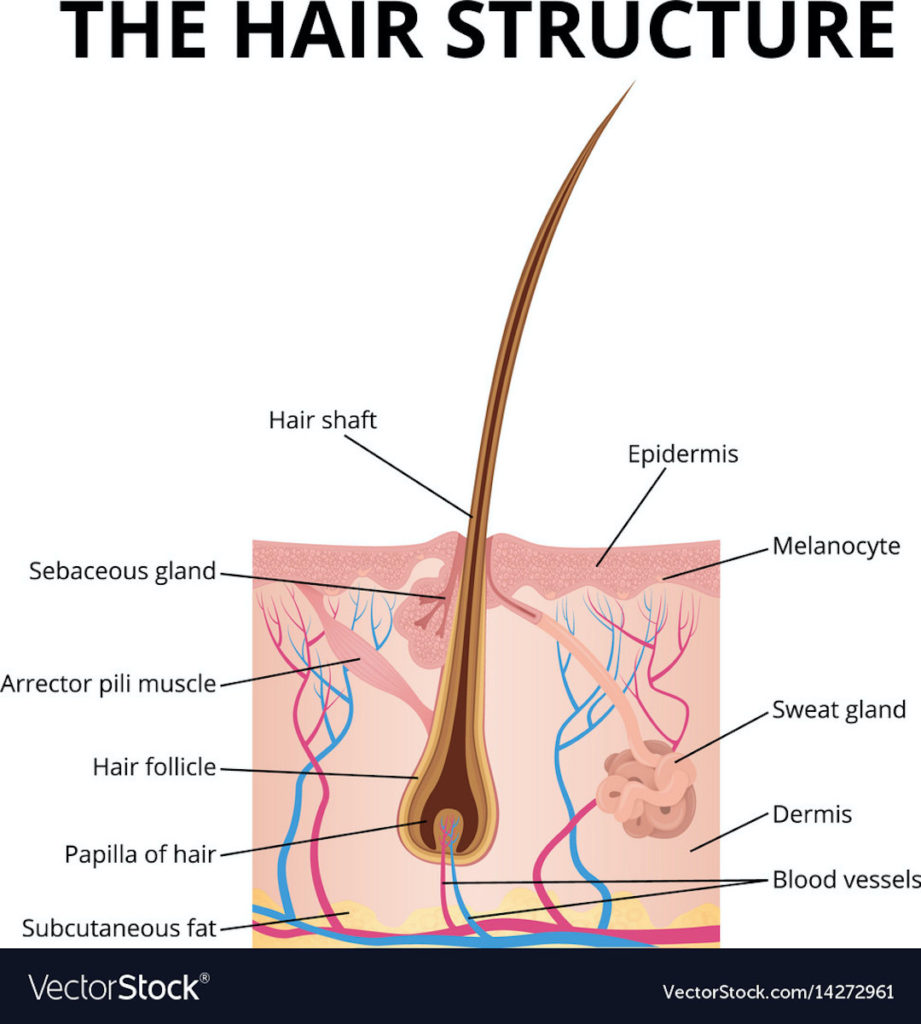
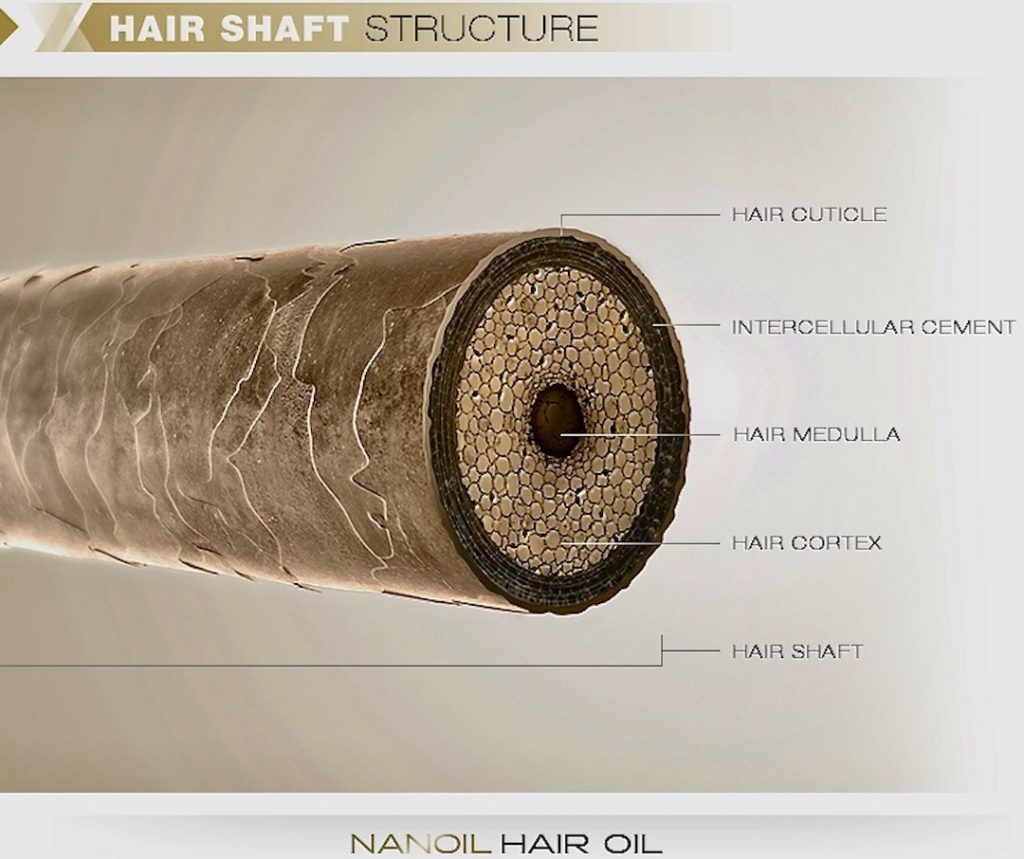
Shaft: The shaft is 2-3 layers of non-living material:
-
- Cuticle: consists of thin, flat cells overlapping like shingles of a roof.
- Cortex: Rod-like bundles of alpha keratin, a protein that strengthens the shaft. This layer also gives hair its color.
- Medulla: Unstructured area in the center – only present in large pili.
People with straight hair have round shafts. People with wavy, curly or coiled hair have oval or flattened shafts. The follicle itself determines the shaft shape and genetics orchestrates the follicle to do its unique thing🤓!

Growth: Each human hair follows its own cycle, at its own pace, including periods of growth and times of quiescence. Think about it! If all our pili were on the same cycle, we would molt! 😳
Angle: You should also know that the shaft does not grow upright; it emerges at a slant.
Try this: Check the angle of growth of your hair: place your forearm on a flat surface with the palm down. Examine your forearm hairs and see that they are angled toward the little finger side of the forearm. That’s the slant!
Arrector Pili Muscle: Microscopic bundles of smooth muscle (meaning these cannot be voluntarily contracted) are attached to the follicle. If these muscles contract, they pull on the follicles causing shafts to stand upright, creating “goose bumps.” Watch this video about the arrector pili muscle for perspective. Contraction happens when we are cold or creeped out! 🥶😱
Contraction of arrector pili muscles also causes oil glands to release their product (sebum) into their respective follicles following the pilus shaft.
Pili are highly valued in many societies which explains the vast sums of money spent on hair products each year; almost 80 million dollars in US in 2019 – down from 90 million spent two years earlier.
Read about Claire’s-Hair in Outlander book. Diana has provided us with ample descriptions of her follicles and shafts. Here are three iconic descriptions of her amazing pili!!! 😲
The wind was rising and the very air of the bedroom was prickly with electricity. I drew the brush through my hair, making the curls snap with static and spring into knots and furious tangles!
… “Mo duinne?”…“It means ’my brown one.’ ”He raised a lock of hair to his lips and smiled, with a look in his eyes that started all the drops of my own blood chasing each other through my veins. Rather a dull color, brown, I’ve always thought,”….”No, I’d not say that, Sassenach. Not dull at all.” He lifted the mass of my hair with both hands and fanned it out. “It’s like the water in a bern, where it ruffles over the stones. Dark in the wavy spots, with bits of silver on the surface where the sun catches it.”
…”Fretful porpentine, was it?” he asked. He tilted his head, examining me inquisitively. “Mmm,” he said, running a hand over his head to smooth down his own hair. “Fretful, at least. You’re a fuzzy wee thing when ye wake, to be sure.” He rolled over toward me, reaching out a hand. “Come here, my wee milkweed.” 🥰
See Claire glorious crown of pili in Outlander, episode 109. Both sides Now!
Grateful for each and every one of my pili! How about you?
The deeply grateful,
Outlander Anatomist
Follow me on:
-
- Twitter: @OutLandAnatomy
- Facebook: OutlandishAnatomyLessons
- Instagram: @outlanderanatomy
- Tumblr: @outlanderanatomy
- Youtube: Outlander Anatomy
Photo Credits: Sony/Starz; www.vectorstock.com; nanoil.com